
The belly button will heal. The great umbilical cord-cutting debate In.
It also highlights evolving data that suggest that delaying cord clamping for 30 to 60 seconds after birth is beneficial to the baby with no measurable negative effects either the baby or the mother.
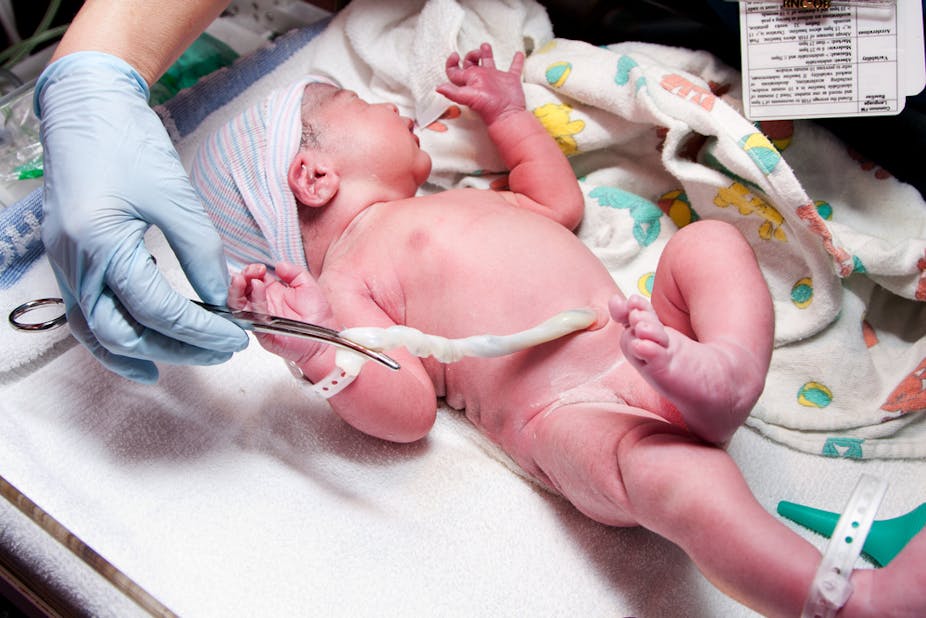
When to cut the umbilical cord after birth. Therefore the cord should be cut before it stops completely normally five minutes after birth. That extra blood supply also means an increase in iron and haemoglobin which are stored in the body. To make the cut the obstetrician applies a clamp just under an inch away from the babys navel and another one about two inches away.
The cut is made between them. This is where the options for the umbilical cord come in. In the past the umbilical cord has been clamped and cut immediately separating the baby from the mother even before the delivery of the placenta happens.
New research in the past decade has shown that there are benefits for both premature and full-term infants to have delayed cord clamping. Immediately after the baby is born before its starts to take its first breath and really get his lungs going the blood is still pumping on the babys side of the placenta. Eventually some of the blood on the babys side comes back to the baby about 80 to 100 cc or three ounces.
Then the umbilical cord stops pulsing and clamps down. Recently there has been a shift to delayed clamping where the umbilical cord is not clamped until at least 1 to 3 minutes after birth. X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the US.
National Institutes of Health Go to source. Benefits for the baby. In most maternity units today normal practice is to clamp and cut the umbilical cord immediately following the birth.
This means babies miss out on between 80 to 100. What Happens to the Umbilical Cord After Birth. The first thing to know is that your midwife will clamp the umbilical cord about 4 cm from the belly button of your baby.
The umbilical stump usually dries out and drops off within 15 days after your baby is born. The belly button will heal. Delayed clamping means the umbilical cord isnt clamped immediately after birth.
Instead its clamped and cut between one and three minutes. The Benefits of Waiting to Cut the Umbilical Cord After Birth Most parents remember the cutting of the umbilical cord after the birth of their baby. Often the father or partner will take that ceremonial role.
In hospitals the cord is very commonly clamped and cut within 30 seconds. Most NHS maternity units still clamp the cord as soon as the child is born though the growing evidence in favour of delayed clamping has prompted a. The mothers side of the placenta is a rubbery-like fleshy placenta.
Both the placenta and the umbilical cord that is attached to the placenta are born about 20 to 30 minutes after the baby was born. This is how the placenta and the attached umbilical cord look after delivery seen from the babys side of. This article provides a brief overview of pros and cons of clamping the cord too early within seconds after birth.
It also highlights evolving data that suggest that delaying cord clamping for 30 to 60 seconds after birth is beneficial to the baby with no measurable negative effects either the baby or the mother. When will the umbilical cord be cut. In most cases the umbilical cord will be cut following birth.
However it does not necessarily have to be cut immediately. According to a review by The Cochrane Library it is possible that keeping your baby connected to their umbilical cord for a period longer than one minute may result in specific health outcomes. Right after birth is a very important magical moment that the mother and baby will never get back the attachment and it should be as immediate and undisturbed as possible.
There is no reason to separate the mother and her baby and there is no reason to cut that cord. The mother and baby should be enjoying beautiful skin to skin contact without any interference. Leave the cord alone.
When the umbilical cord is not cut it naturally seals off after about an hour after birth. The umbilical cord and attached placenta will fully detach from the baby anywhere from two to 10 days. Medical studies have shown the positive effects of delayed cord cutting The World Health Organization recommends delayed umbilical cord cutting between 1 to 3.
The umbilical cord is the lifeline of survival for the developing baby. It is the conduit of blood oxygen and nutrients and the means by which waste is extracted. There continues to be some function of the umbilical cord after birth that can last on average for up to about five minutes after delivery.
The common practice is to clamp and cut. In most Western countries including the United States the cord is clamped immediately after birth. Usually between 10 to 15 seconds after.
The great umbilical cord-cutting debate In. The umbilical cord will be pulsating quickly when the baby is born. However after some time it will turn white and limp.
At that point your baby has retrieved all the blood it needs from the placenta. Cutting the cord too quickly will deprive your newborn of too much blood. Thats why its so important to delay cord clamping.
You can wait until the placenta is delivered before you get the scissors. But you can actually.