
Both private and public cord blood banks have developed in. The storage of umbilical cord cells has not been without controversy and there is a rapidly growing private sector involvement.
New parents have the option of storing their newborns cord blood at a private cord blood bank or donating it to a public cord blood bank.
Umbilical cord banking controversy. Addressing this controversy is important in moving research and treatments forward in an ethical manner. When a baby is born parents are asked what they would like to do with the umbilical cord blood. Their choices are typically to discard it along with the placenta donate to a public cord bank or pay to store it in a bank for private use.
Like any insurance cord-blood banking isnt cheap. Banks initially charge from 1000 to 2000 to collect and process the stem-cell units which are stored for a familys exclusive use. Compelled by a pamphlet in their doctors office they decided to store Zoes umbilical-cord blood banking its precious stem cells for potentially lifesaving medical use in the future.
The storage of umbilical cord cells has not been without controversy and there is a rapidly growing private sector involvement. A number of ethical issues. Umbilical Cord Cell Banking.
A Surprisingly Controversial Issue. DOI link for Umbilical Cord Cell Banking. A Surprisingly Controversial Issue.
The controversy over private banking Though public and private banks provide a similar service the ability to store cord blood their methods and standards can differ substantially. Although commercial cord blood banks often bill their services as biological insurance against future diseases the blood doesnt often get used. One study says the chance that a child will.
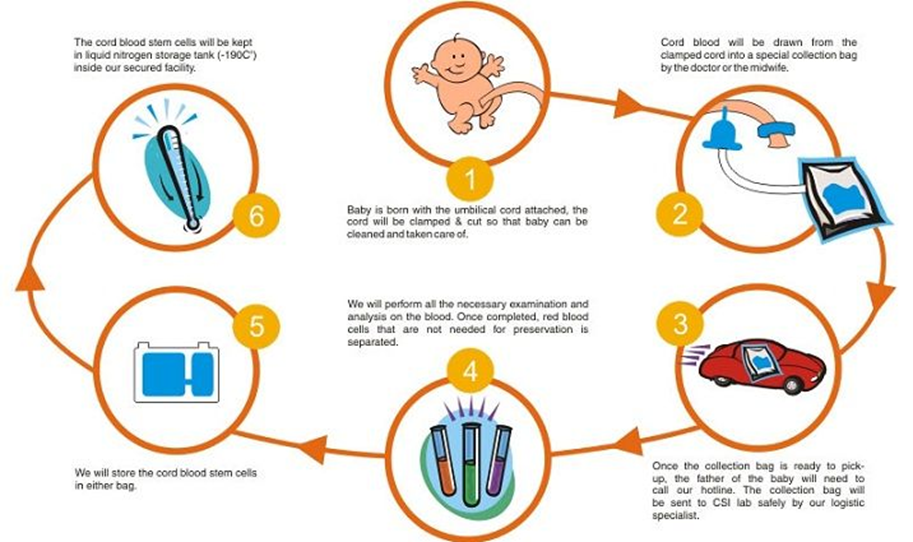
Once the blood is removed from the umbilical cord your doctor will cut a segment of the tissue thoroughly clean it and place it in a collection cup. What happens after the collection. Once the collection is complete your babys cord blood and cord tissue stem cells will be transported to a lab for processing and storage.
When researching cord blood banks be sure to choose a facility accredited. Over umbilical cord blood banking suggests that it is largely compatible with religion but bioethical inquiry should not be confined to controversy as the grounds for compatibility between medical innovation and religion are also worth investigating. A cord blood bank is a facility which stores umbilical cord blood for future use.
Both private and public cord blood banks have developed in. Controversy on the most effective and economically sustainable model for banking and storing an optimal UCB product continues to persist. Cord blood banking and transplantation of cord blood stem cells has advanced rapidly over the initial 25 years as more than 30 000 patients have benefited from the therapy.
New concepts on the use. Thats the controversial question being asked about a potentially life-saving practice in which cord blood – the blood collected from a newborns placenta and umbilical cord – is stored for. The controversy surrounding private banking of umbilical cord blood units CBU as a safeguard against future malignancy or other lifethreatening conditions raises many questions in pediatric clinical practice.
Recent favorable experiences with autologous transplantation for severe aplastic anemia using privately stored CBU suggested a possible. Cord blood banking is a procedure in which cord blood a rich source of stem cells is taken from the umbilical cord after delivery and used for research or preserved for possible use in a stem cell transplant. Collecting cord blood poses few if any risks.
Growth of blood banking. Umbilical cord blood is rich in stem cells that can be used to treat patients with abnormal haematopoietic cell lines childhood leukaemia or metabolic diseases. 1 Bone marrow is used for this purpose but cord blood is cheaper and easier to obtain and less likely to trigger a harmful immune response or rejection in the recipient.
There is a very good reason why the question of banking umbilical cord blood is such an important one. The use of cord blood or more accurately the multipotent possibly pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells which are present within cord blood is a modern medical advance that has greatly improved outcomes in a subset of very ill patients. The controversy surrounding private banking of umbilical cord blood units CBU as a safeguard against future malignancy or other life-threatening conditions raises many questions in pediatric clinical practice.
Recent favorable experiences with autologous transplan-tation for severe aplastic anemia using privately stored CBU. Umbilical cord blood UBC can be viewed as the most promising source of stem cells in which collection cost is minimal and its benefits are immense. Public cord blood banking is supported by the medical community.
However private cord blood banking is generally not recommended unless there is a family history of specific genetic diseases. New parents have the option of storing their newborns cord blood at a private cord blood bank or donating it to a public cord blood bank. The cost of private cord blood banking is approximately 2000 for.