HSV-1 and HSV-2 infection puts newborns at high risk for developing severe and life-threatening symptoms including. Women who acquire herpes during pregnancy or experience reactivation of the virus during pregnancy have the potential to transmit HSV-1 to their baby.

The risk with recurrent herpes is very low.
Hsv1 and pregnancy. HSV-1 Pregnancy. Can Pregnant Women Infect Their Babies. Women who acquire herpes during pregnancy or experience reactivation of the virus during pregnancy have the potential to transmit HSV-1 to their baby.
Of the babies who do contract herpes 85 become infected when passing through the birth canal during delivery. In response to these questions we summarize previous reports on herpes simplex virus 1 HSV-1 oral disease in pregnancy and briefly present 2 cases of primary gingivostomatitis in the first trimester of pregnancy resulting in a favourable outcome for both mother and infant. ACOG has updated the guidelines for management of genital herpes in pregnancy.
HSV transmission is via direct contact with an incubation period of 2 to 12 days. There are two types of HSV. Most cases genital herpes are caused by HSV-2.
HSV-1 infection at least in the first trimester and the rarity of potentially severe CNS HSV-1 infection the following concerns should be kept in mind in relation to pregnancy. The risk of acquisition and development of fulminant HSV-1 disease which is higher than in the general. Genital herpes is one of the most common health conditions in the US.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC estimates that 1 in 6 people between the ages of 14 and 49 have it. Approximately 22 of pregnant women in the US. Two percent contract it during pregnancy thats 1 in 50 pregnant women.
If the mothers infection is a true primary she has no previous antibodies to either HSV-1 or HSV-2 and she seroconverts becomes HSV positive at the end of pregnancy the risk of transmission can be as high as 50 according to research by Brown and others. The risk is also high if she has prior infection with HSV-1 but not HSV-2. Herpes is a lifelong infection without a cure though medications can help manage symptoms and outbreaks even during pregnancy.
Herpes is caused by two types of the herpes simplex viruses HSV. HSV-1 which usually causes cold sores or blisters around the mouth though it can be spread to the genital area during oral sex. A mother can infect their baby during delivery sometimes fatally.
But if a woman had genital herpes before getting pregnant or if they are first infected early in pregnancy the chance that their. You can still have a vaginal outbreak with HSV-1 I delivered my 1st daughter vaginally. The only way you can transmit it to the baby is if you have an active outbreak during delivery.
2-3 weeks before delivery your doctor will put you on a suppression medication and you can deliver a healthy baby. Causes of cold sores in pregnancy Cold sores are caused by a virus the herpes simplex virus HSV. Of the two types of HSV cold sores are generally caused by.
Primary genital herpes infection in pregnancy is associated with an increased risk for perinatal transmission compared to recurrent HSV1 2. HSV IgG antibody status can help to clarify whether the herpes episode is primary. Determining whether any HSV antibody present is of the same type as the HSV genital lesion assists with risk stratification.
Genital herpes simplex virus HSV infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections occurring in one in five women in the. Similarly asymptomatic viral shedding is rare in genital HSV-1 infection. The odds are very highly in your and your babys favor.
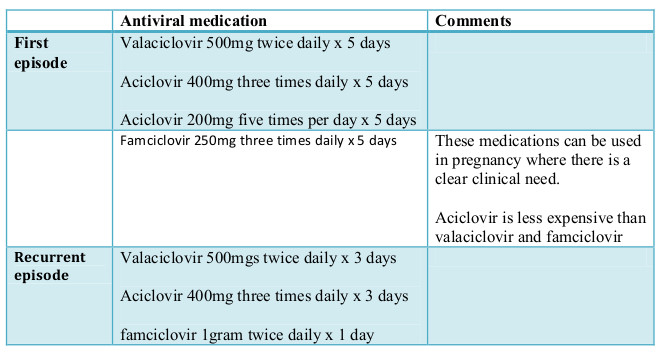
Most neonatal herpes especially the serious cases occur when a woman acquires genital HSV infection during pregnancy especially during the last 2-3 months. The risk with recurrent herpes is very low. Acyclovir can be administered orally to pregnant women with first-episode genital herpes or recurrent herpes and should be administered IV to pregnant women with severe HSV infection.
Suppressive acyclovir treatment late in pregnancy reduces the frequency of cesarean delivery among women who have recurrent genital herpes by diminishing the frequency of recurrences at term 378. Herpes is a very common sexually transmitted disease. In fact it is estimated that 20 to 25 of pregnant women are carriers of the herpes virus.
The vast majority of them will have children without experiencing any herpes-related complications for their babies. HSV-1 and HSV-2 infection puts newborns at high risk for developing severe and life-threatening symptoms including. Fatal organ damage including the liver lungs and heart Serious viral infections such as viral meningitis Recurrent sores on the skin eyes genitals or mouth.
Herpes simplex is most often spread to an infant during birth if the mother has HSV in the birth canal during delivery. HSV can also be spread to the baby if he or she is kissed by someone with an active cold sore. In rare instances HSV may be spread by touch if someone touches an active cold sore and then immediately touches the baby.
The risk of maternal-fetal transmission MFT is high in primary genital herpes infection if acquired at the time of labour about 50 or within 6 weeks prior to delivery. Delivery by caesarean section is indicated. Women with a past history of genital herpes and no recurrences in pregnancy can be reassured that the risk of MFT is extremely low.