
Tweetable abstract This study demonstrates that delayed cord clamping is safe in mothers with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. Healthcare professionals midwives and obstetricians encourage women to have skin-to-skin contact with their babies as soon as possible after the birth.
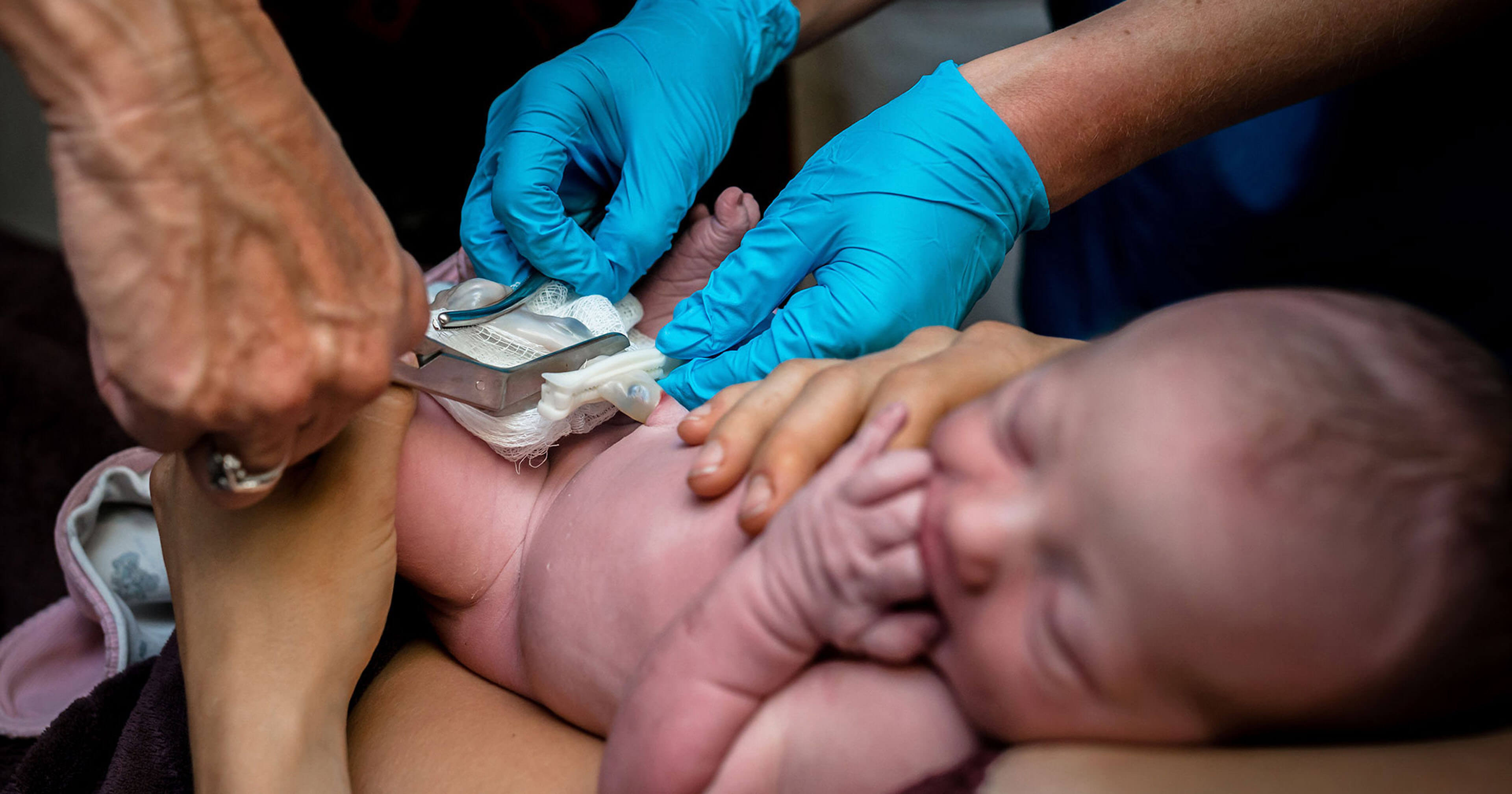
It used to be that once baby was born the umbilical cord was clamped and cut almost immediately.
Delayed cord clamping and skin to skin. This belief based on studies conducted 35 years ago meant babies who underwent delayed cord clamping were denied important skin to skin contact with the mother immediately after birth. No significant differences between groups were found regarding neonatal tests for SARS-CoV-2. No confirmed cases of vertical transmission were detected.
The percentage of mothers who made skin-to-skin contact within the first 24 hours after delivery was significantly higher in the DCC group 843 versus 459. Breastfeeding in the immediate postpartum period was also significantly higher in the. Lets talk about delayed cord clamping yall.
It used to be that once baby was born the umbilical cord was clamped and cut almost immediately. That was just the standard of care in most US hospitals. There is now a more widespread understanding that when a baby is born about 13 of their blood is not inside their body but is inside the placenta the organ that filters cleans the blood.
To assess if delayed cord clamping and immediate skin to skin contact at caesarean section would result in better neonatal behaviour and infant development. 377 To be revised based on interim analyses Inclusion criteria. Pulse Oximetry in newborns with delayed cord clamping and immediate skin-to-skin contact March 2014 Archives of Disease in Childhood - Fetal and Neonatal Edition 994.
Delayed cord clamping combined with immediate skin-to-skin contact after birth ensures that the intricate process of bonding and breastfeeding get the best possible start. John Stevenson wrote in Midwifery Today that clamping and cutting the cord at once deprives baby of up to a cupful of its own blood which is very wrong. A delay in cord clamping has been linked to a higher risk of jaundice.
But delayed clampings benefits may outweigh this risk as long as phototherapy treatment for jaundice is available. And in most cases this does not interfere with early care including drying and stimulating for the first breath and immediate skin-to-skin contact. Healthcare professionals midwives and obstetricians encourage women to have skin-to-skin contact with their babies as soon as possible after the birth.
Commissioners clinical commissioning groups specify and check that service providers have protocols in place to ensure that women are encouraged to have skin-to-skin contact with their babies as soon as possible after the birth. Some centres have suppressed or substantially minimised delayed cord clamping DCC motherinfant skintoskin contact and breastfeeding. 11 15 However WHO 16 and diverse scientific societies Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC 17 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists ACOG 18 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE 19 Spanish.
Perinatal outcomes when performing ECC or DCC and skin-to-skin contact or breastfeeding. Keywords Breastfeeding COVID-19 safety SARS-CoV-2 skin-to-skin umbilical cord clamping vertical transmission. Tweetable abstract This study demonstrates that delayed cord clamping is safe in mothers with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Mised placental circulation delayed cord clamp-ing should occur for at least 30 to 60 seconds for most vigorous term and preterm newborns Raju Singhal 2012. Delayed cord clamp-ing provides increased initial blood volume that favors improved hemoglobin levels Ultee van der Deure Swart Lasham. Delayed cord clamping DCC and immediate skin to skin contact ISSC was not routine management What this study adds Defined reference ranges can be used for evaluating infants born after uncomplicated birth but higher SpO 2 and lower HR were observed in the first minutes.
Minutes before clamping and cutting the cord. The baby can still be placed skin to skin for example on the mothers chest if the cord is long enough. If the baby is higher than the level of the placenta blood flow is slightly slower as the blood has to be pushed uphill.
Delayed cord clamping DCC and immediate skin to skin contact ISSC is routine management. Design Prospective observational study. Setting and patients Infants born vaginally after uncomplicated.
Posts about skin-to-skin contact written by Kate Emerson. Cord clamping information research. Evidence Base and Links.
Birth plans and stories. Blog Articles archives. This tag is associated with 1 post Mother and babypositioning after birth Posted by Kate Emerson.
الترجمة باللغة العربيةBrought to you byMother Child. Your trusted source for family care adviceعالم الأم والطفل. Delayed umbilical cord clamping may reduce a preterm babys need for blood transfusions and risk of bleeding in the brain and of a serious bowel complication called necrotizing enterocolitis.
It may also help increase a preterm babys blood pressure. However delayed umbilical cord clamping is also associated with jaundice yellowing of the skin caused by too much bilirubin in the infants blood. The immediate benefits of delayed umbilical cord clamping.