How long to wait. Sometimes the cord is wrapped very tightly around the babys neck and needs to be cut to allow the baby to be delivered.
It may also include not clamping or cutting the umbilical cord until after the placenta is delivered.
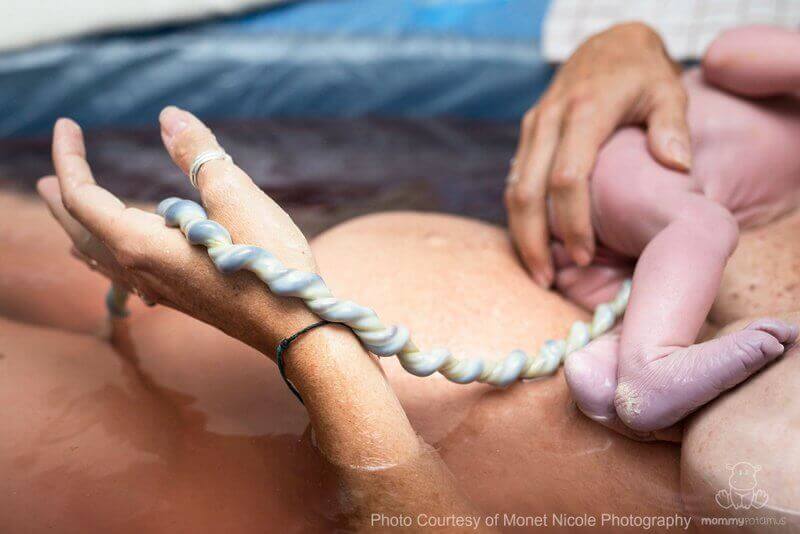
Cutting the umbilical cord after the placenta is delivered. After the baby is born and before the placenta is delivered the umbilical cord is clamped in two places and cut between the clamps. In a typical birth the umbilical cord is cut shortly after the baby is delivered severing the child from the placenta which is an organ thats responsible for providing nutrients and oxygen to. This is where the options for the umbilical cord come in.
In the past the umbilical cord has been clamped and cut immediately separating the baby from the mother even before the delivery of the placenta happens. New research in the past decade has shown that there are benefits for both premature and full-term infants to have delayed cord clamping. Its a simple technique performed by gently grasping the uncut umbilical cord and squeezing several times from the placenta towards the infant.
In contrast to delayed cord clamping milking provides a placental transfusion without postponing resuscitation and can be completed as quickly as immediate cord clamping. The umbilical cord carries blood and nutrients from the placenta to the infant in pregnancy. It is what ties the mother and child together in utero providing a pathway for fluid and nutrient exchange.
Cutting or clamping the cord physically separates the child from the placenta after childbirth. The biomedical process of birth is to cut. Delayed clamping means the umbilical cord isnt clamped immediately after birth.
Instead its clamped and cut between one and three minutes after birth. Currently most hospitals in the United. This study clearly states.
Early clamping of the umbilical cord at birth a practice developed without adequate evidence causes neonatal blood volume to vary 25 to 40. Cord circulation continues for several minutes after birth and placental transfusion results in approximately 30 more blood volume. When the baby is born the cord is clamped and cut.
Recent Canadian research has shown that there are health benefits to delaying the cutting of the cord for about two minutes. If you have opted for cord-blood banking blood will be painlessly withdrawn from the cord after its cut but usually before the placenta is delivered. And then theres the perspective expressed by the International Childbirth Education Association which is that Delayed cord clamping DCC is a practice by which the umbilical cord is not clamped or cut until after it stops pulsating.
It may also include not clamping or cutting the umbilical cord until after the placenta is delivered 3. Some conditions affecting the mom would be if the mom has hemorrhaging and the placenta needs to be removed immediately or if the placenta has prematurely separated during delivery. Sometimes the cord is wrapped very tightly around the babys neck and needs to be cut to allow the baby to be delivered.
Waiting to cut the umbilical cord also doesnt affect the results of the Apgar test which is performed five minutes after birth. However if the mother has been sedated during childbirth the umbilical cord should be cut immediately. This way the medication doesnt continue to pass to the baby.
How long to wait. After the greenish colored placenta is delivered the mother should sever the umbilical cord with her teeth. If she does not do this within a few minutes you will need to help her.
You will need to tie the cord however prior to cutting it. You should always wash your hands with soap and hot water before handling newborn puppies. After birth a clamp is put on the cord and it is cut so that the baby is no longer attached to the placenta.
This procedure is one of the oldest involved in birth. Cutting the umbilical cord. Cutting the cord used to be one of the first things most healthcare practitioners did when a baby was born whether through the uterus or a C-section.
Within 15 to20 seconds of a baby entering the world practitioners used a clamp to stop the blood flow between baby and mom and then she or your partner if he or she wishes cut the cord with the snip of a scissors. There is another recommendation that expressed by the International Childbirth Education Association which is that Delayed cord clamping DCC is a practice by which the umbilical cord is not clamped or cut until after it stops pulsating. It may also include not clamping or cutting the umbilical cord until after the placenta is delivered.
When the umbilical cord is not cut it naturally seals off after about an hour after birth. The umbilical cord and attached placenta will fully detach from the baby anywhere from two to 10 days after the birth. On one hand we want the safest possible delivery.
The third stage of labour can be managed actively or by expectant management where the umbilical cord remains attached to the baby until after delivery of the placenta. Blood within the placental compartment drains into the baby. Placental cord drainage involves clamping and cutting of the umbilical cord after the birth of a baby and then.