The reliability validity and efficacy of electronic fetal monitoring EFM remain matters of. Continuous electronic fetal monitoring was developed in the 1960s to assist in the diagnosis of fetal hypoxia during labor.

According to the 2007 Listening to Mother Survey 87 of US.
Continuous electronic fetal monitoring. Continuous electronic heart rate monitoring for fetal assessment during labor The only clinically significant benefit from the use of routine continuous EFM was in the reduction of neonatal seizures. Electronic fetal monitoring is used to screen for transitions in the continuum of fetal health to fetal stress and subsequently to distress. The diagnosis of fetal distress is complex and influenced by multiple factors.
Factors that influence the fetal heart rate are incompletely understood. Continuous electronic fetal monitoring. Contradictions between practice and research.
1Maternal-Child Health Department School of Nursing at Boston College Chestnut Hill MA USA. The reliability validity and efficacy of electronic fetal monitoring EFM remain matters of. Continuous electronic fetal monitoring during labour is a screening test.
It aims to identify fetuses at risk of developing intrapartum hypoxic damage. Note regarding the term continuous EFM. There are two main ways to continuously monitor the fetal heartbeat electronically.
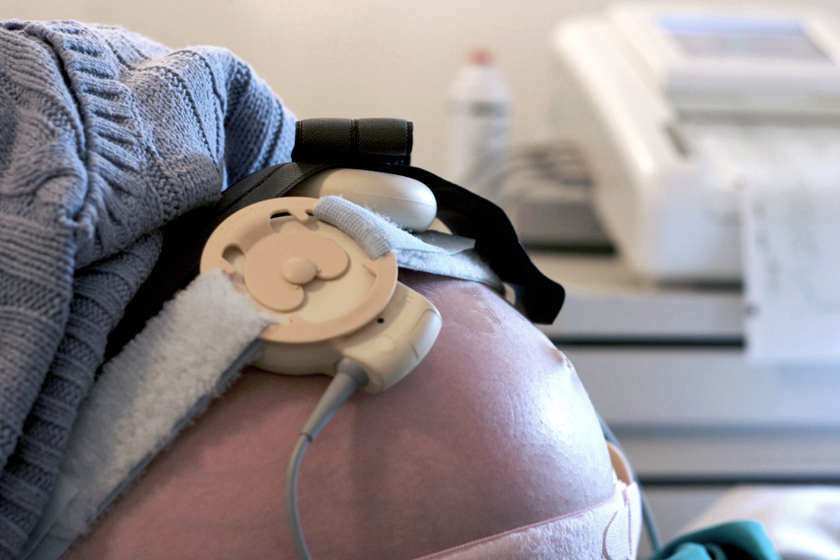
1 internal in which an electrode is attached to the scalp of the unborn baby and 2 external which customarily uses a Doppler ultrasound transducer strapped to the maternal abdomen along with a second device that measures uterine contractions. Youll have continuous electronic fetal monitoring if. You have pregnancy complications or develop any during labor.
You have a preexisting medical condition such as chronic hypertension diabetes or heart disease. You get an epidural. You require oxytocin Pitocin to induce or augment labor.
Even if your pregnancy and labor are low risk chances are high youll receive continuous fetal monitoring. Continuous electronic fetal monitoring is the continuous monitoring of fluctuations of the fetal heart rate FHR in relation to maternal contractions and is considered standard practice during. Electronic fetal monitoring is often used during labour to detect unborn babies at risk of brain damage neonatal encephalopathy from a lack of oxygen hypoxia.
Continuous electronic fetal monitoring was developed in the 1960s to assist in the diagnosis of fetal hypoxia during labor. Continuous electronic fetal monitoring has been shown to reduce the. Intrapartum Electronic Fetal Monitoring Lisa A.
Ruth Part 1 Introduction and Overview This module will provide clinicians with practical information on intrapartum fetal monitoring with a primary focus on electronic fetal monitoring EFM. The module is divided into six sections. Part 1 provides an overview of intrapartum fetal monitoring and includes information.
Continuous cardiotocography CTG as a form of electronic fetal monitoring EFM for fetal assessment during labour. Continuous cardiotocography during labour is associated with a reduction in neonatal seizures but no significant differences in cerebral palsy infant mortality or other standard measures of neonatal well-being. Continuous cardiotocography CTG as a form of electronic fetal monitoring EFM for fetal assessment during labour What is the issue.
Is continuous cardiotocography CTG to electronically monitor babies heartbeats and wellbeing during labour better at identifying problems than listening intermittently. Why is this important. Continuous Electronic Fetal Monitoring Statistics The Cochrane database of systematic reviews and the WHO Reproductive Health Library RHL reports a total of 12 studies involving over 30000 women.
The purpose of the studies was to find the risks associated with continuous EFM. Electronic fetal monitoring EFM also called cardiotocography CTG is when the babys heart rate is monitored with an ultrasound machine while the mothers contractions are monitored with a pressure sensor Alfirevic et al. Both of these sensors are linked to a recording machine which shows a print-out or computer screen of the babys.
According to the 2007 Listening to Mother Survey 87 of US. Described experiencing continuous electronic fetal monitoring during labor Declercq Sakala et al. However just because the monitoring is continuous does not mean that a clinician is continuously watching the monitor.
We are delighted to confirm the publication of the NGA-developed NICE exceptional review of the fetal monitoring recommendations in CG190. Recommendations in CG190 have been exceptionally reviewed and adapted in response to stakeholder feedback and implementation issues taking account of new evidence. Further details can be found via the NICE website where the updated recommendations are.
Electronic fetal monitoring is used to screen for transitions in the continuum of fetal health to fetal stress and subsequently to distress. The diagnosis of fetal distress is complex and influenced by multiple factors. Factors that influence the fetal heart rate are incompletely understood.